#humanBehaviour #demandmodelling #Prediction
"The willing to move"
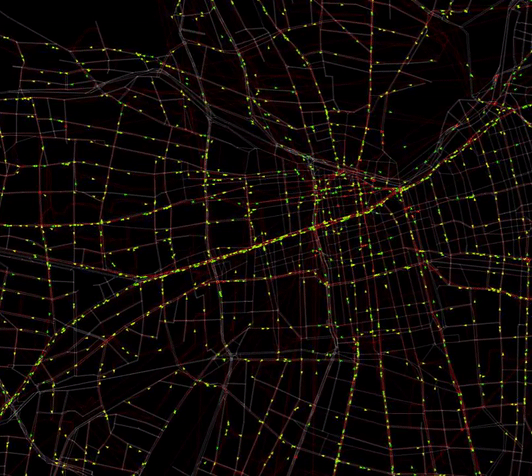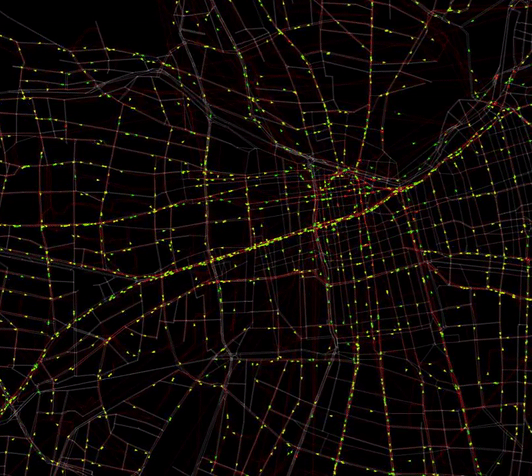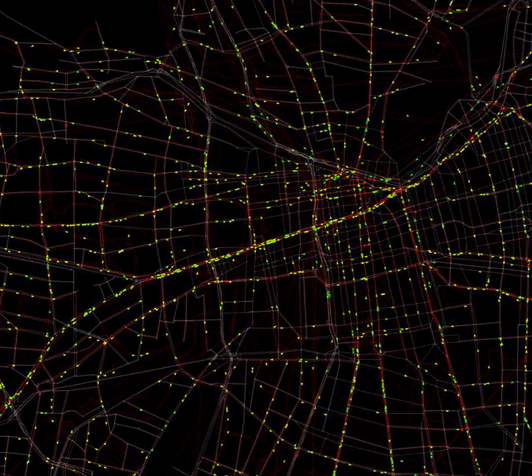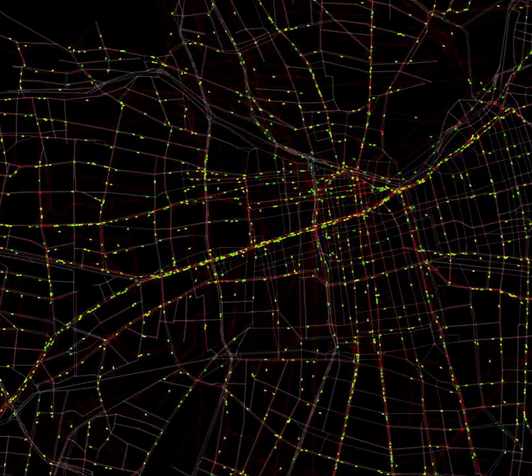
Predictive demand is crucial when planning the city. Knowing how drivers, pedestrians, or traffic itself will behave after the implementation of certain measures constitutes a supporting tool for city decision makers. In this sense, Movēre’s simulation algorithms and analysis are adapted for each case and performed under MATSim (ETH Zurich developed) open-source framework, as a demonstrated reliable tool for implementing large-scale agent-based transport simulations.
Multi Agent Modelling
Framework for demand-modelling are some of the solutions in movēre to simulate human behaviour and support planning decisions. As agent-based modelling, the simulations have the ability to predict decisions per unit (commuter) and its interaction with other agents in the model.
Analysis are powered by MATSim, a ETHZ developed open-source software to implement large-scale agent-based transport (Public and Private) simulations
The FaLC Simulation Tool
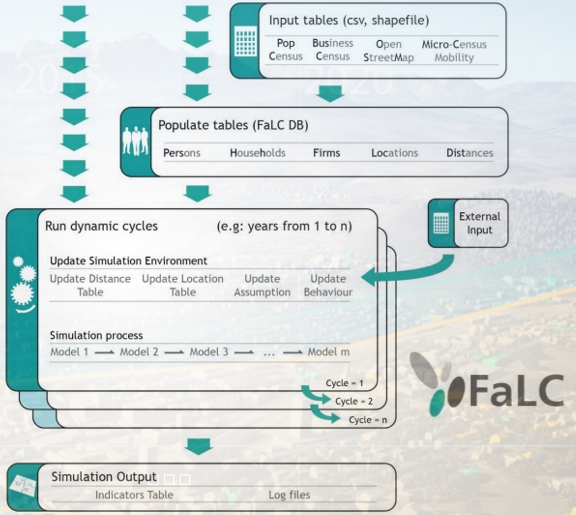
Following Mr. Balz R. Bodenmann's Dissertation at the ETH, Zürich "Location choice of firms with special emphasis on spatial accessibility", and together with the creation of ETHZ Spin-off RegioConcept AG, Mr. Bodenmann created and led a dedicated team of GIS specialyst (Alexandra Zeiler), Java Programmers (János Bode & Peter Furtak) and a Transport Modeler/Data Analyst (Breogan Sanchez) among others, to develop a powerful non-concurrent Falicity Locations Choice Simulation Tool (FaLC).
As a multi-agent based system, in FaLC, the "agents" (individuals, households or businesses) which are accuratelly simulated persons taking age, workplace or place of residence into account, determine their future, enabling the tool to simulate the (future) development of population, jobs, construction, real estate demand, transport (integrates a multi-transport model), and their interaction effects such as relocation of households and companies, with results even closer to the reality.
Bodenmann B.R., B. Sanchez, J. Bode, A. Zeiler, M. Kuljovský, P. Furták, G. Sarlas and K.W. Axhausen (2014) Planning for the Future: A Land-use and Transport Interaction Model for Switzerland, paper presented at the 54th ERSA Congress, St. Petersburg, August 2014. >>Download
Bodenmann, B.R., J. Bode, B. Sanchez, A. Zeiler, P. Furták, M. Kuljovsky, I. Vecchi and K.W. Axhausen (2015) An Integrated Land Use Model for Switzerland, Detailed Description of the FaLC Template 2015, FaLC Working Paper, 03, regioConcept and IVT, Herisau/Zürich. >>Download
Experiences
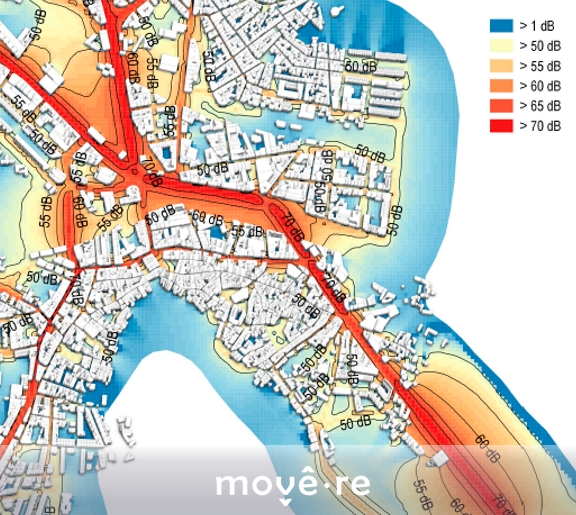
Furthermore, modelling goes beyond the traffic itself and support further analysis such as road collisions analysis or noise modelling
All in all, modelling support decisions by evaluating existing conditions and projecting future effects and needs